Calculations
Material calculations define how much of each material is consumed based on input values (variables) from the configurator form. The system allows you to create flexible, condition-based formulas that adapt to different scenarios.
Overview
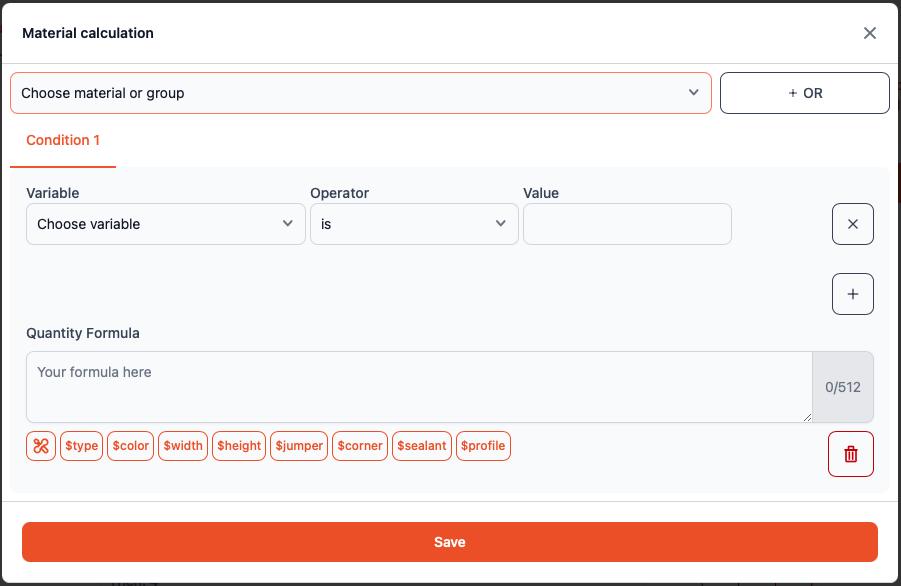
A material calculation consists of:
- Material or Material Group – The target material for which consumption is calculated
- Conditional Logic – OR conditions that are evaluated sequentially
- Quantity Formulas – Mathematical expressions that determine material usage
Structure & Components
1. Material Selection
Choose the specific material or material group from the dropdown menu.
2. Condition Logic
The system supports sophisticated conditional logic:
- Up to 5 OR condition blocks – Each represents an alternative scenario
- Up to 5 AND conditions per OR block – All must be true for the block to execute
- Sequential evaluation – The system processes OR blocks in order and stops at the first match
Condition Fields (AND Logic)
Each AND condition consists of three parts:
- Variable – Select from previously defined variables (e.g.,
$width,$height,$color) - Operator – Choose the comparison method:
is– Exact matchis not– Not equal togreater than– Numerical comparison (>)less than– Numerical comparison (<)include– Value exists in a listnot include– Value does not exist in a list
- Value – The comparison value or literal
3. Quantity Formula
The quantity formula defines material consumption when conditions are met. The formula editor supports:
Variables
Use any defined variables with the $ prefix:
$width, $height, $color, $material_type
Mathematical Operations
Standard arithmetic operators and functions:
+, -, *, /, (), abs, round, ceil, floor, trunc, max, min
Advanced Functions
Trigonometric and logarithmic functions:
sin, cos, tan, asin, acos, atan, atan2, pow, sqrt, exp, log, log10, random
Conditional Expressions
JavaScript-style ternary operators for complex logic:
condition ? value_if_true : value_if_false
Formula Examples
Basic calculation:
($width - 38) / 1000
Conditional calculation:
($width >= 700 || $height >= 1700) ? 4 : 2
Complex formula with multiple conditions:
$color == "premium" ? ($width * $height * 1.5) : ($width * $height * 1.2)
How It Works
- Input Processing – Variables are populated from the configurator form
- Condition Evaluation – OR blocks are checked sequentially
- Formula Execution – When conditions match, the quantity formula calculates material usage
- Result Application – The calculated quantity is applied to the selected material
Evaluation Flow
FOR each OR condition block:
IF all AND conditions are true (or no AND conditions exist):
EXECUTE quantity formula
STOP processing
ELSE:
CONTINUE to next OR block
Best Practices
- Start with simple conditions and build complexity gradually
- Use descriptive variable names to maintain clarity
- Test formulas thoroughly with different input combinations
- Consider edge cases in your conditional logic
- Use comments in complex formulas when possible
Troubleshooting
- Division by zero – Always validate denominators in formulas
- Undefined variables – Ensure all variables are properly defined
- Syntax errors – Check parentheses and operator usage
- Type mismatches – Verify variable types match operator expectations
Material calculations provide powerful flexibility for accurate material consumption estimates. The combination of conditional logic and mathematical formulas allows you to handle complex scenarios while maintaining system performance and accuracy.